Joint Distributions#
In this lab, we will implement a multilevel logistic regression model using the tensorflow_probability’s JointDistribution API.
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_probability as tfp
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
from sklearn.neighbors import KernelDensity
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.style.use("ggplot")
tfd = tfp.distributions
2023-02-15 13:28:15.021355: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:193] This TensorFlow binary is optimized with oneAPI Deep Neural Network Library (oneDNN) to use the following CPU instructions in performance-critical operations: AVX2 FMA
To enable them in other operations, rebuild TensorFlow with the appropriate compiler flags.
2023-02-15 13:28:15.106212: W tensorflow/compiler/xla/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'libcudart.so.11.0'; dlerror: libcudart.so.11.0: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
2023-02-15 13:28:15.106229: I tensorflow/compiler/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cudart_stub.cc:29] Ignore above cudart dlerror if you do not have a GPU set up on your machine.
2023-02-15 13:28:15.668431: W tensorflow/compiler/xla/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'libnvinfer.so.7'; dlerror: libnvinfer.so.7: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
2023-02-15 13:28:15.668490: W tensorflow/compiler/xla/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'libnvinfer_plugin.so.7'; dlerror: libnvinfer_plugin.so.7: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
2023-02-15 13:28:15.668497: W tensorflow/compiler/tf2tensorrt/utils/py_utils.cc:38] TF-TRT Warning: Cannot dlopen some TensorRT libraries. If you would like to use Nvidia GPU with TensorRT, please make sure the missing libraries mentioned above are installed properly.
## TEACHER
import inspect
import init; init.init(force_download=False); init.get_weblink()
## TEACHER
from local.lib.rlxmoocapi import submit, session
session.LoginSequence(
endpoint=init.endpoint,
course_id=init.course_id,
lab_id="L04.01.03",
varname="teacher"
);
We’ll use the following synthetic dataset:
n_features = 2
n_classes = 3
X, y = make_blobs(
n_samples=500,
n_features=n_features,
centers=n_classes,
random_state=42
)
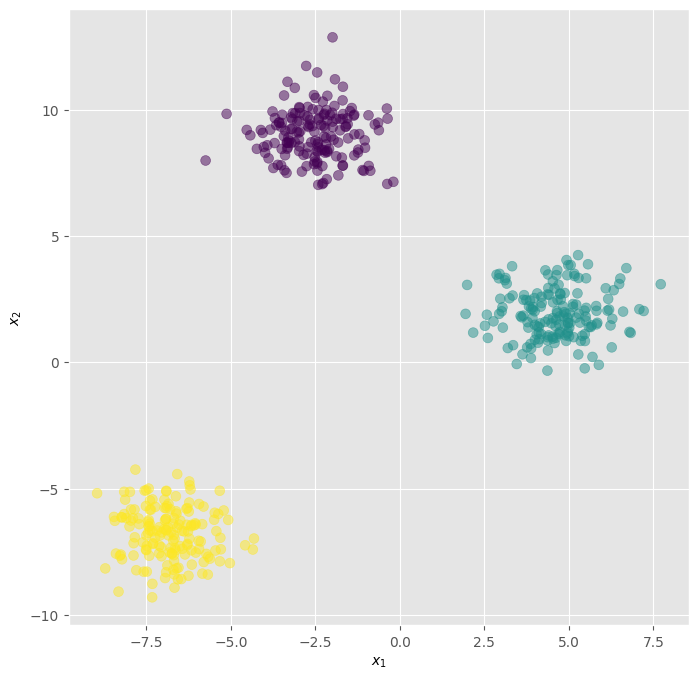
We can visualize the data:
## KEEPOUTPUT
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(8, 8))
ax.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, s=50, cmap="viridis", alpha=0.5)
ax.set_xlabel("$x_1$")
ax.set_ylabel("$x_2$")
Text(0, 0.5, '$x_2$')
Task 1: Logistic Regression#
In this task, you must define a logistic regression model using the JointDistributionNamed API, you must implement the following model:
The model must have the following distributions: w, b, and y:
def prob_log_regression(x, n_features, n_classes):
# YOUR CODE HERE
model = ...
return model
## TEACHER
def prob_log_regression(x, n_features, n_classes):
model = tfd.JointDistributionNamedAutoBatched({
"w": tfd.Normal(loc=tf.zeros(shape=(n_features, n_classes)), scale=1.),
"b": tfd.Normal(loc=tf.zeros(shape=(n_classes, )), scale=1.),
"y": lambda b, w: tfd.Independent(
tfd.Categorical(logits=x @ w + b),
reinterpreted_batch_ndims=1
)
}
)
return model
You can use the model to generate samples:
## KEEPOUTPUT
model = prob_log_regression(X, n_features, n_classes)
samples = model.sample(1)
print(samples["y"].shape)
(1, 500)
## TEACHER
def grader1(functions, variables, caller_userid):
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_probability as tfp
tfd = tfp.distributions
namespace = locals()
for f in functions.values():
exec(f, namespace)
n_features = 2
n_classes = 3
n_samples = 500
X, y = make_blobs(
n_samples=n_samples,
n_features=n_features,
centers=n_classes,
random_state=42
)
prob_log_regression = namespace["prob_log_regression"]
model_student = prob_log_regression(X, n_features, n_classes)
msg = "Validating probabilistic model...</br>"
if not isinstance(model_student, tfd.JointDistribution):
msg += "<b>Your model is not a joint distribution.</b></br>"
return 0, msg
dists = model_student.sample_distributions()[0]
expected_dists = {
"w": {
"type": tfd.Normal,
"batch_shape": [n_features, n_classes],
"event_shape": []
},
"b": {
"type": tfd.Normal,
"batch_shape": [n_classes],
"event_shape": []
},
"y": {
"type": tfd.Independent,
"batch_shape": [],
"event_shape": [n_samples],
}
}
for param, values in expected_dists.items():
if param not in dists:
msg += f"<b>Your model doesn't contain the distribution '{param}'</b></br>"
return 0, msg
if not isinstance(dists[param], values["type"]):
msg += f"<b>The distribution '{param}' is incorrect.</b>"
return 0, msg
if list(dists[param].batch_shape) != values["batch_shape"]:
msg += f"<b>The distribution '{param}' has a wrong batch_shape.</b>"
return 0, msg
if list(dists[param].event_shape) != values["event_shape"]:
msg += f"<b>The distribution '{param}' has a wrong event_shape.</b>"
return 0, msg
return 5, msg + "<b>Success!</b>"
Use the following cell to grade your code:
## TEACHER
source_functions = ["prob_log_regression"]
source_variables = []
res = teacher.run_grader_locally("grader1", source_functions, source_variables, locals())
display(res)
grade: 5
grader message
Validating probabilistic model...Success!
teacher.set_grader(
teacher.course_id, "L04.01.03", "T1",
inspect.getsource(grader1), "grader1",
source_functions, source_variables
)
student.submit_task(namespace=globals(), task_id="T1");
Task 2: Markov Chain Monte Carlo#
Implement the mcmc function to train the model, you must use a Markov Chain Monte Carlo Strategy, We recommend using the NoUTurnSampler but feel free to experiment with the sampler.
## TEACHER
@tf.function
def mcmc(
model,
y,
n_features,
n_classes,
num_samples,
burning_steps,
step_size=1e-3
):
def log_prob(w, b):
return model.log_prob(w=w, b=b, y=y)
kernel = tfp.mcmc.NoUTurnSampler(
target_log_prob_fn=log_prob,
step_size=step_size
)
return tfp.mcmc.sample_chain(
num_results=num_samples,
num_burnin_steps=burning_steps,
current_state=[
tf.ones(shape=(n_features, n_classes)),
tf.ones(n_classes)
],
kernel=kernel,
trace_fn=lambda _, results: results.target_log_prob
)
samples, log_probs = mcmc(
model=model,
y=y,
n_features=n_features,
n_classes=n_classes,
num_samples=100,
burning_steps=50,
)
WARNING:tensorflow:From /home/juselara/repositories/teaching/udea/ppml.dev/.venv/lib/python3.9/site-packages/tensorflow/python/autograph/pyct/static_analysis/liveness.py:83: Analyzer.lamba_check (from tensorflow.python.autograph.pyct.static_analysis.liveness) is deprecated and will be removed after 2023-09-23.
Instructions for updating:
Lambda fuctions will be no more assumed to be used in the statement where they are used, or at least in the same block. https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/56089
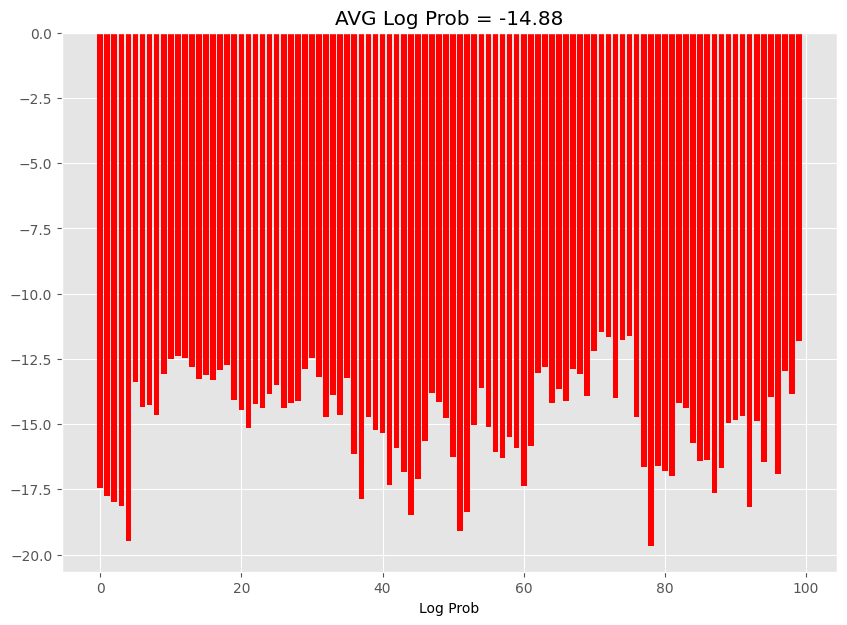
Use the following cell to generate a visualization of the log_probs, it must look similar to:
Note: The results may vary but the log-probs range bust be similar to the figure, and the average, must be close.
## KEEPOUTPUT
log_probs_viz = log_probs.numpy()
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(10, 7))
ax.bar(np.arange(log_probs_viz.size), log_probs_viz, color="r")
ax.set_xlabel("Sample")
ax.set_xlabel("Log Prob")
ax.set_title(f"AVG Log Prob = {log_probs_viz.mean():.2f}")
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'AVG Log Prob = -14.88')
def grader2(functions, variables, caller_userid):
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import tensorflow_probability as tfp
tf.random.set_seed(0)
tfd = tfp.distributions
namespace = locals()
for f in functions.values():
exec(f, namespace)
# compare descriptive stats using the same base model.
n_features = 2
n_classes = 2
n_gen_samples = 100
burnout = 100
X = np.array([
[0, 0],
[0, 1],
[1, 0],
[1, 1]
] * 10, dtype="float32")
y = {
"and": np.array([0, 0, 0, 1] * 10),
"or": np.array([0, 1, 1, 1] * 10),
}
mcmc = namespace["mcmc"]
msg = "Validating mcmc procedure...</br>"
for case, y_i in y.items():
model = tfd.JointDistributionNamedAutoBatched({
"w": tfd.Normal(loc=tf.zeros(shape=(n_features, n_classes)), scale=1.),
"b": tfd.Normal(loc=tf.zeros(shape=(n_classes, )), scale=1.),
"y": lambda b, w: tfd.Independent(
tfd.Categorical(logits=X @ w + b),
reinterpreted_batch_ndims=1
)
})
samples, log_probs = mcmc(
model=model,
y=y_i,
n_features=n_features,
n_classes=n_classes,
num_samples=n_gen_samples,
burning_steps=burnout,
)
if samples[0].shape != tf.TensorShape([n_gen_samples, n_features, n_classes]):
msg += "<b>Your function returns samples with wrong w shapes.</b></br>"
return 0, msg
if samples[1].shape != tf.TensorShape([n_gen_samples, n_classes]):
msg += "<b>Your function returns samples with wrong b shapes.</b></br>"
return 0, msg
if log_probs.shape != tf.TensorShape([n_gen_samples]):
msg += "<b>Your function returns log_probs with wrong shape.</b></br>"
return 0, msg
w = samples[0].numpy().mean(axis=0)
b = samples[1].numpy().mean(axis=0)
y_pred = np.argmax(X @ w + b, axis=1)
if (y_pred == y_i).sum() / y_i.size < 0.9:
msg += "<b>The mcmc function does not optimize the specified model.</b></br>"
msg += str(y_pred)
msg += str(y_i)
return 0, msg
return 5, msg + "<b>Success!</b>"
## TEACHER
source_functions = ["mcmc"]
source_variables = []
res = teacher.run_grader_locally("grader2", source_functions, source_variables, locals())
display(res)
grade: 5
grader message
Validating mcmc procedure...Success!
## TEACHER
teacher.set_grader(
teacher.course_id, "L04.01.03", "T2",
inspect.getsource(grader2), "grader2",
source_functions, source_variables
)
student.submit_task(namespace=globals(), task_id="T2");
Task 3: Kernel Density Estimation#
Compute the Maximum Aposteriori predictions of the parameters as follows:
You must use KernelDensity for the estimation of the MAP parameters.
def kde(w_samples, b_samples, x, kernel="gaussian", bandwidth=0.1):
# YOUR CODE HERE
preds = ...
return preds
## TEACHER
def kde(w_samples, b_samples, x, kernel="gaussian", bandwidth=0.1):
flat_w = w_samples.reshape(
(-1, np.prod(w_samples.shape[1:]))
)
w_densities = (
KernelDensity(kernel=kernel, bandwidth=bandwidth)
.fit(flat_w)
.score_samples(flat_w)
)
idx = np.argmax(w_densities)
w_map = w_samples[idx]
flat_b = b_samples.reshape(
(-1, np.prod(b_samples.shape[1:]))
)
b_densities = (
KernelDensity(kernel=kernel, bandwidth=bandwidth)
.fit(flat_b)
.score_samples(flat_b)
)
idx = np.argmax(b_densities)
b_map = b_samples[idx]
probs = tf.nn.softmax(x @ w_map + b_map)
preds = np.argmax(probs, axis=1)
return preds
Let’s generate some predictions:
## KEEPOUTPUT
preds = kde(samples[0].numpy(), samples[1].numpy(), X)
print(preds)
[2 1 1 0 1 1 2 1 1 2 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 2 2 0 1 0 1 2 2 1 1 2 2 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1
1 2 2 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 2 2 0 2 2 1 0 0 2 1 2 2 0 1 2 1 2 1 2 0 1 1 1 1 2
0 2 0 1 0 0 2 0 1 0 2 2 2 2 1 0 2 1 0 1 1 2 0 0 0 2 1 0 0 2 2 0 0 2 0 2 2
2 2 2 2 1 0 2 1 2 0 0 1 1 2 1 0 1 2 2 2 1 1 2 1 2 2 2 1 0 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 0
0 0 1 2 1 1 0 2 0 2 1 1 2 2 0 0 2 0 0 1 2 2 2 0 0 2 2 0 0 1 1 1 0 2 0 0 2
2 0 1 0 2 2 2 2 2 0 1 0 0 2 1 0 0 2 2 1 2 1 0 0 2 2 1 2 0 0 2 0 2 0 1 1 0
2 0 1 0 0 2 1 1 1 1 0 2 2 2 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 2 2 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 2
0 0 0 2 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 2 0 0 0 0 2 2 0 1 0 0 2 0 1 2 1 1 2 0 0 0 2 0
2 1 1 0 1 2 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 2 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 0 2 1 1 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 0
2 0 2 0 0 2 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 2 2 1 2 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 2 0 1 1 0 2
0 2 0 1 2 0 2 1 2 2 1 2 0 1 2 2 0 1 2 1 2 1 0 0 1 2 1 0 0 0 1 2 1 0 1 1 2
2 1 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 2 2 1 0 1 2 0 0 1 2 1 1 2 2 1 2 0 0 2 1 2 0
0 2 1 2 0 0 1 2 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 2 1 2 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 2 2 0 0 2 2 0 2 1 1 0
0 2 2 0 1 2 2 1 2 2 0 2 1 0 2 0 1 2 1]
def grader3(functions, variables, caller_userid):
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
from sklearn.neighbors import KernelDensity
namespace = locals()
for f in functions.values():
exec(f, namespace)
kde_student = namespace["kde"]
def kde(w_samples, b_samples, x, kernel="gaussian", bandwidth=0.1):
flat_w = w_samples.reshape(
(-1, np.prod(w_samples.shape[1:]))
)
w_densities = (
KernelDensity(kernel=kernel, bandwidth=bandwidth)
.fit(flat_w)
.score_samples(flat_w)
)
idx = np.argmax(w_densities)
w_map = w_samples[idx]
flat_b = b_samples.reshape(
(-1, np.prod(b_samples.shape[1:]))
)
b_densities = (
KernelDensity(kernel=kernel, bandwidth=bandwidth)
.fit(flat_b)
.score_samples(flat_b)
)
idx = np.argmax(b_densities)
b_map = b_samples[idx]
probs = tf.nn.softmax(x @ w_map + b_map)
preds = np.argmax(probs, axis=1)
return preds
msg = "Testing your kde function with 10 random trials</br>"
for _ in range(10):
n_samples = np.random.randint(1, 100)
n_gen_samples = np.random.randint(1, 10)
num_features = np.random.randint(2, 10)
num_classes = np.random.randint(2, 10)
samples_w = np.random.normal(size=(n_gen_samples, num_features, num_classes))
samples_b = np.random.normal(size=(n_gen_samples, num_classes))
x, _ = make_blobs(n_samples, num_features, centers=num_classes)
preds_student = kde_student(samples_w, samples_b, x)
preds_teacher = kde(samples_w, samples_b, x)
if not np.allclose(preds_student, preds_teacher):
msg += "The MAP predictions do not match the expected results."
return 0, msg
return 5, msg + "<b>Success!</b>"
## TEACHER
source_functions = ["kde"]
source_variables = []
res = teacher.run_grader_locally("grader3", source_functions, source_variables, locals())
display(res)
grade: 5
grader message
Testing your kde function with 10 random trialsSuccess!
## TEACHER
teacher.set_grader(
teacher.course_id, "L04.01.03", "T3",
inspect.getsource(grader3), "grader3",
source_functions, source_variables
)
student.submit_task(namespace=globals(), task_id="T3");
Let’s evaluate this model:
## KEEPOUTPUT
print(classification_report(y, preds))
precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 1.00 1.00 167
1 1.00 1.00 1.00 167
2 1.00 1.00 1.00 166
accuracy 1.00 500
macro avg 1.00 1.00 1.00 500
weighted avg 1.00 1.00 1.00 500

